CalPeak Power LLC
Owned by Middle River Power
Operated by NAES Corp
242 MW, four simple-cycle peaking plants (Border, Enterprise, Panoche, and Vaca Dixon), each consisting of one FT8-2 TwinPac generating unit operating on natural gas, located in San Diego, Calif
Plant manager: Ramiro GonzalezMidway Peaking LLC
Owned by Middle River Power
Operated by NAES Corp
120 MW, simple-cycle peaking plant consisting of two FT8-3 SwiftPac generating units operating on natural gas, located in Firebaugh, Calif
Plant manager: Ramiro Gonzalez
Challenge. The CalPeak Power and Midway plants are remotely operated, manned during normal working hours, and unmanned on nights and weekends. The six generating units are dispersed throughout California, with a spread of 544 miles. Some units are located in very rural areas.
CEMS calibrations are conducted daily, regardless of work schedules. Equipment issues affecting calibrations can go undetected until “it’s too late,” resulting in an environmental notice of violation and/or forced outage. Incidents can include the following:
- Failure of regulator valves.
- Pressure gage issues.
- Plant staff closing cylinder valves to prevent gas from escaping because of an unidentified leak.
Solution. Middle River Power (MRP) engaged WestAir Gases and Equipment, Fontana, Calif, to install a Pulsa real-time gas and tank level monitoring system. It uses sensors that are attached to the high side of the gas regulator (Fig 1) and a cellular service to communicate externally and transmit data (Fig 2). Internally it connects via Bluetooth® or WiFi to each individual pressure sensor to collect data at intervals of every few minutes.
The system also offers a cellphone app through which users can scan the sensor QR code and access status information. Plus, the application monitors connectivity health and sends notifications if a sensor is not reading data or becomes disconnected.
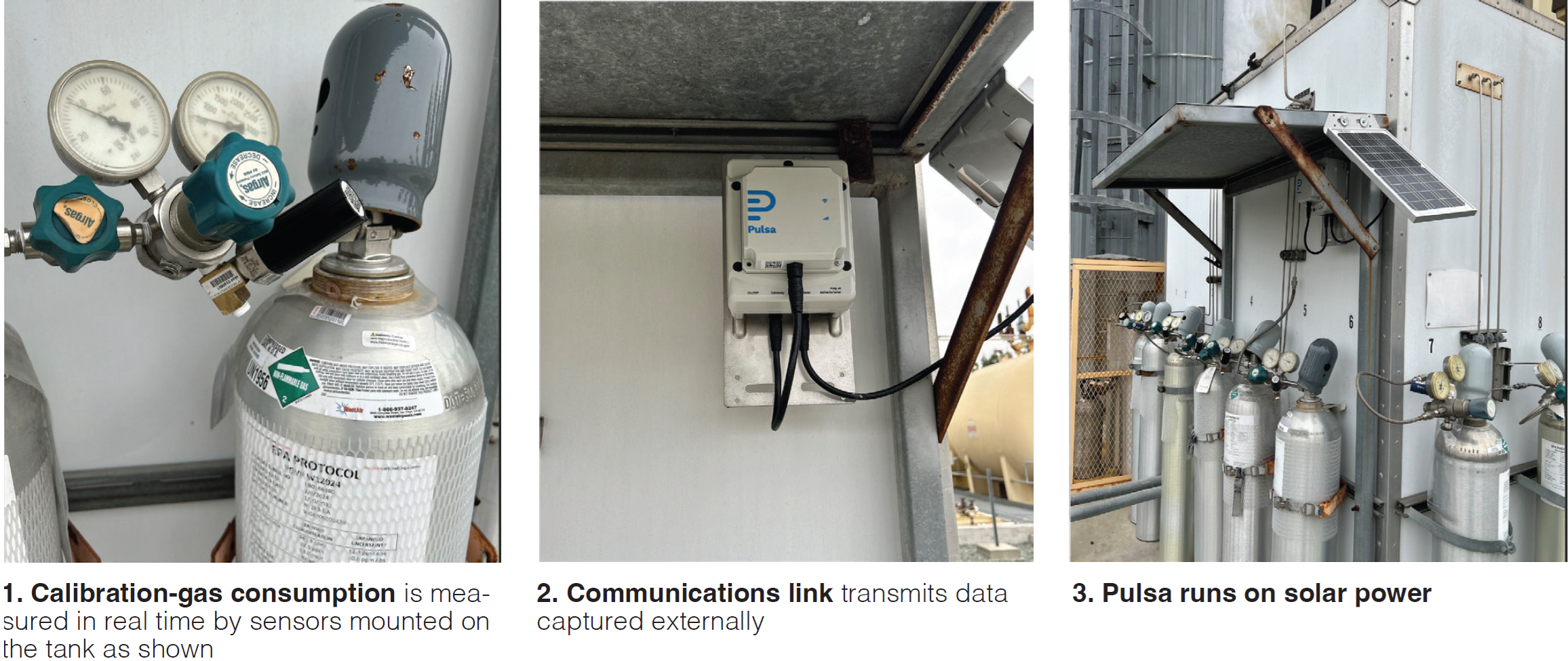
Pulsa is powered by solar energy (Fig 3) and features a battery life of 40 days (when fully charged) before depletion. Alternative power-supply configurations can be implemented as needed.
Pulsa’s sensor/software technology allows staff to remotely measure consumption of calibration gas in real time, providing numerous advantages, such as these:
- Remote monitoring of system readiness.
- Continual pressure monitoring.
- Alarm notification based on cylinder pressure.
- Alarm notification for rapid discharge (leak identification).
- Automatic ordering and supplier notification based on calculated remaining capacity of cylinders.
- Preventive planning and reaction—especially considering that sites are not staffed 24/7. In the past, MRP has experienced issues with leaks developing during weekends when there was no one onsite. They were discovered only when someone returned or when gas was required for a run but couldn’t be delivered.
Results. The project easily met expectations—or surpassed them. The 24/7 monitoring presence provides peace of mind both when sites are manned as well as in the remote management of unmanned sites.
The safety net protects against incidents that could result in potentially large, unplanned expenses, such as these:
- Fines related to any potential notices of violation or correction. Prior to adopting the Pulsa technology, MRP had an incident that led to the filing of a Breakdown Report to the Air District. A bottle had drained over the weekend, leaving the unit without gas during operation. Since installing Pulsa, none of the company’s generating units has encountered a similar situation. However, there have been low-pressure alarms, but they are programmed to trigger in advance, giving staff ample time to correct the cause. Personnel are currently monitoring the low-pressure alarms and may adjust their settings as needed to better suit requirements.
- Lost revenue from plant downtime attributed to failed calibrations caused by leaks or other issues.
Project participants:
Plant personnel